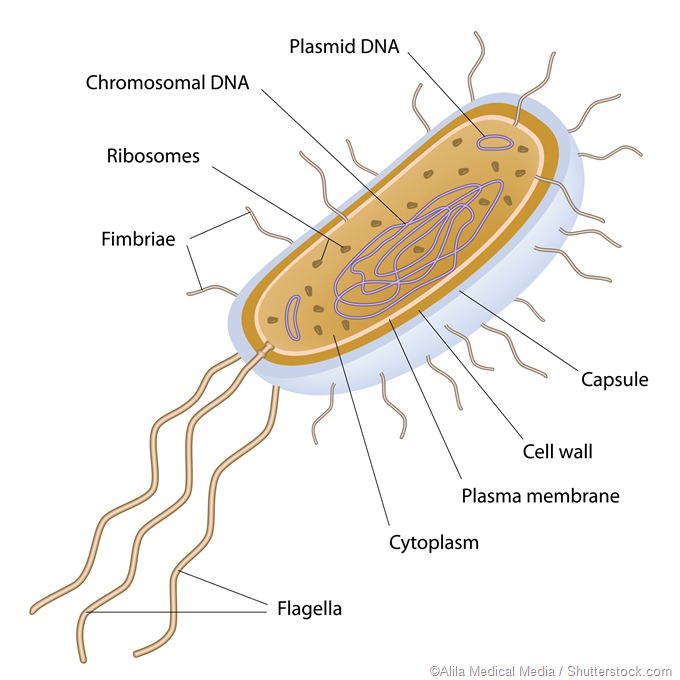
Cytoplasm It refers to the fluid found inside the plasma membrane which constitutes a few cell organelles. Describe the structure and function of six different structures found on the exterior of a bacterial cell.

The Structure Of Prokaryotes Biology I
Flagella help prokaryotes move in their environment.

. Hair-like projections called fimbriae. A prokaryotic cell does not have a nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic mitochondria are thought be derived from bacteria in this group.
Prokaryotes are the smallest and most common microorganism they are single celled and lack a nucleus Describe the three main cell shapes of prokaryotes. Three primary features found in prokaryotic cells are. Is 7-8µ in diameter.
It helps in moisture retention protects the cell when. They may be spherical rod-shaped or spiral. Protists are the eukaryotic predominantly unicellula View the full answer.
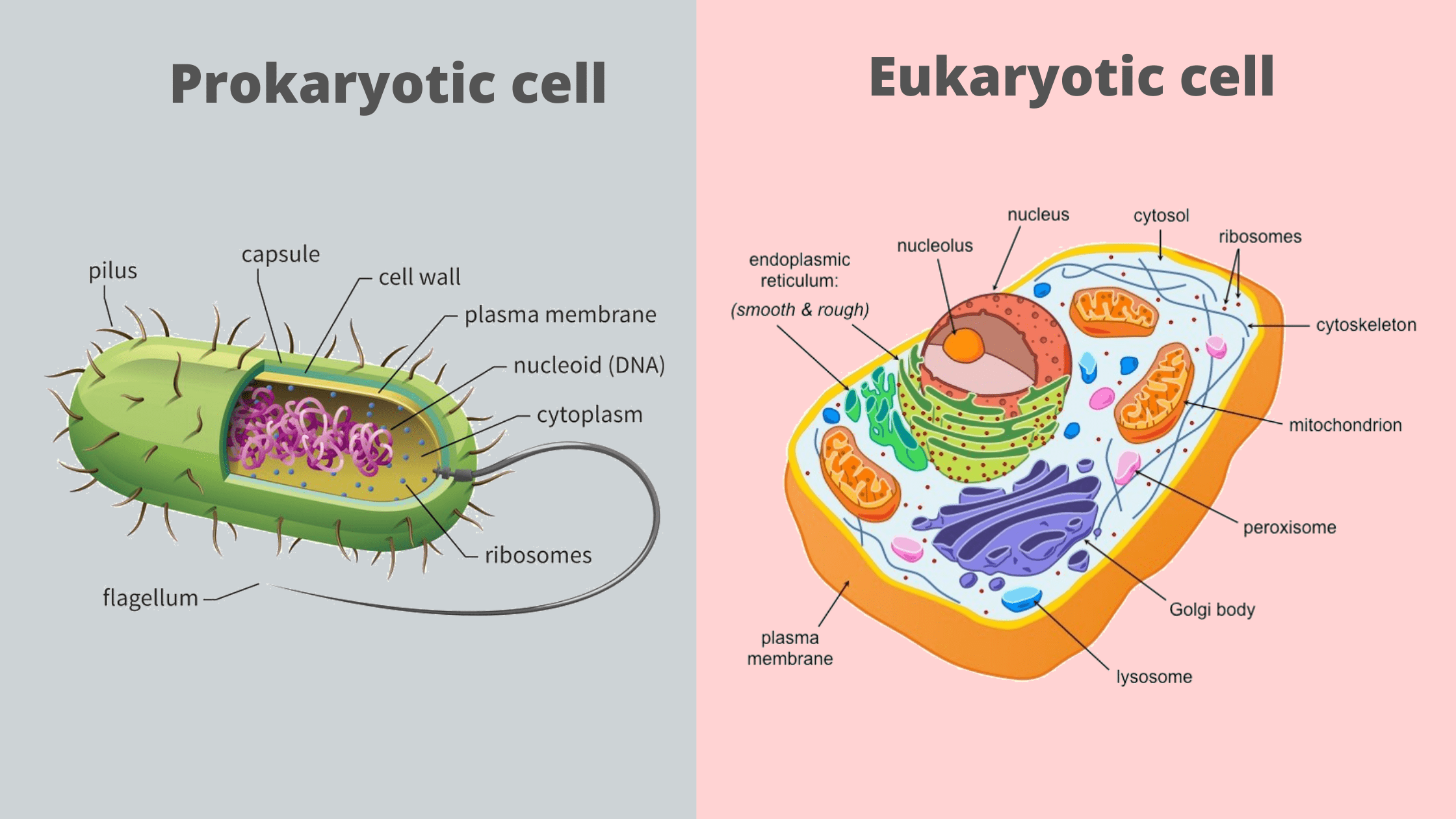
Trace the pathway in a eukaryotic cell by which a secreted protein would be produced starting in the nucleus Why do we not find cells the size of a house. Common prokaryotic cell types. Flagella and pili are not found in all prokaryotes.
A cocci or spherical a pair is shown. B bacilli or rod-shaped. Prokaryotes fall into three basic categories based on their shape visualized here using scanning electron microscopy.
It is a thin lipid bilayer. Plasma Membrane It refers to the outer membrane which separates the inner environment from the external environment. 1000 µ in length.
Prokaryotes fall into three basic categories based on their shape visualized here using scanning electron microscopy. Describe the three main cell shapes of prokaryotes. The first phylum described is proteobacteria which includes five classes alpha beta gamma delta and epsilon.
B bacilli or rod-shaped. And c spirilli or spiral-shaped. Like eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm a gel-like substance that makes up the filling of the cell and a cytoskeleton that holds components of the cell in place.
The rod-shaped are called bacilli. The spherical-shaped are called colli. Prokaryotic Cell Structure Capsule.
Most species of Alpha Proteobacteria are photoautotrophic but some are symbionts of plants and animals and others are pathogens. Rod shape spiral coccus that is round shape are the 3 shapes that prokaryotic cells can be. Found in some bacterial cells this additional outer covering protects the cell when it is engulfed by other.
The cellwalls are of two types gram positive and gram negative. Describe a typical animal cell and be able to differentiate it from a plant cell. A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows.
Describe the structure and. The length of acellular diatoms is about 100µ And the size of Amoeba proteus is 1 mm. It is selectively permeable.
There are different shapes of prokaryotic cells. They are also used to help cells attach to one another. Prokaryotic cells are very small 5-5 um and are much less complex than eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotes come in various shapes but many fall into three categories. Differentiate a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell. Prokaryotic cells have various shapes.
The long nerve is also an example of the extremes in cell sizes the range of which is quite remarkable in the. Arrow_forward Distinguish a typical bacterial cell from a typical plant or animal cell in terms of cell shapes and arrangements size and cell structures. Cocci spherical bacilli rod-shaped and spirilli spiral-shaped Figure 1.
However the genetic material is present in a region in the cytoplasm known as the nucleoid. Out of all the structures the two selected structuresare the cell- wall and endospores. The cell- wall of bacterial cellsis found in three distinct shapes such as spherical spiral and rod shaped.
Describe the three main shapes of bacterial cells. Cocci - spherical Bacilli - rod shaped Spirochaete - spiral shaped Vibrio - comma shaped. Usually the vast majority of cells lie in the range of 05 to 20µ in diameter.
Prokaryotes fall into three basic categories based on their shape visualized here using scanning electron microscopy. A cocci or spherical a pair is shown. The cell wall is an outer covering that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape.
Describe the three different types of vacuoles typically found in eukaryotic cells. Describe the three main cell shapes of prokaryotes The rod-shaped are called bacilli The spherical-shaped are called colli The corkscrew-shaped are called spirilla Distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative Under a microscope if bacteria are Gram-positive it is violet if it is Gram-negative it is red. Cocci or coccus for one cell are round cells occasionally slightly flattened when adjacent to every other.
The three main shape of the bacteria are coccus spherical bacillus rod-shaped and spiral twisted. Flagella and Pili - protein structures which project from the cells surface which are used primarily for movement. The capsule enables prokaryotes to adhere to their substrate or to other individuals in a colony and shields pathogenic prokaryotes from attacks by a hosts immune system.
Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes which are organelles that produce proteins and vacuoles small spaces in cells that store nutrients and help eliminate waste. The cellwall of the bacterial cellsis composed of the proteins and polysaccharides. B bacilli or rod-shaped.
Capsule It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells in addition to the cell wall. List and describe the functions of the three types of cytoskeletal filaments. Envelope - a cell wall which covers a plasma membrane.
All prokaryotic cell shares four common components- 1. The size of human RBC. The four basic shapes are.
And c spirilli or spiral-shaped. Bacteria and archaebacteria are prokaryotes. A cocci or spherical a pair is shown.
Some prokaryotes have external structures that extend beyond the cell wall.

Prokaryotic Cell Definition Examples Structure Biology Dictionary
0 Comments